NoSQL
Let’s see some highlight points about NoSQL and just a few points about the relational databases to remember what is this.
Relational
- SQL to manage data
- Use of tables
- Use of predefined scheme
- Guarantees of ACID
- Recommended when is required many transactions with columns as return
- Relational DB typically provide consistency and availability, but not partition tolerance.[1]
- Horizontal partition increases operational overhead
NoSQL
- High performance
- The relationship between the data is different
- Unstructured or semi-structured data
- Usually don't provide ACID guarantees
- Patterns implemented to attack the consistency issue: Sagas, CQRS, and asynchronous messaging.
- Dynamic scheme
- Data storage in different ways which can have different porpose:
- Benefits
- Flexible data models
- Horizontal scaling
- Fast queries
- Easy for developers
- Recommended when is required big volume of data and constant changes
- NoSQL databases typically support high availability and partition tolerance.[2]
MongoDB
MongoDB is a cross-platform, document oriented database that provides, high performance, high availability, and easy scalability. MongoDB works on concept of collection and document.[2]
It 's a NoSQL database. The MongoDB has support to ACID guarantees. The main document about this tool you can find here.
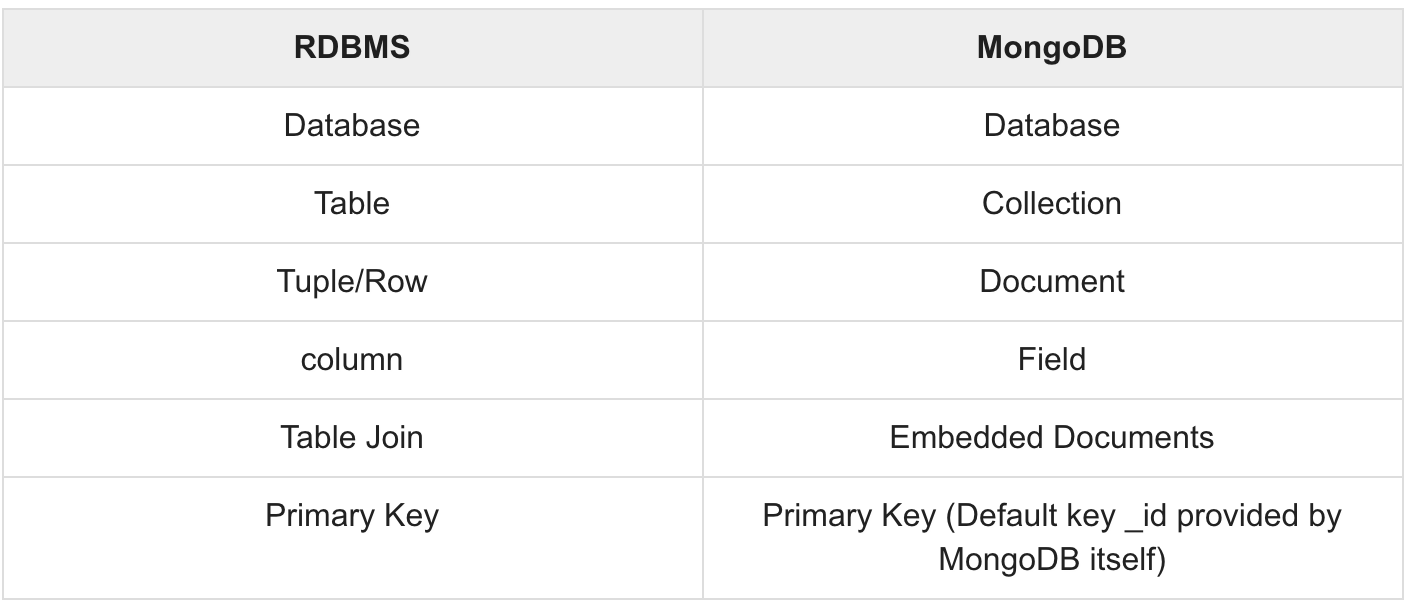
Resource: tutorialspoint
The types of documents support by mongoDB is JSON/BSON. As well, MongoDB use the key-pair concept. A simplistic way: Key is an identifiers and the documents are the values.
MongoDB’s document values allow nested key-value structures, allowing not only for accessing data by key in a global sense, but accessing and manipulating data associated with keys within documents, and even creating indexes that allow fast retrieval by these secondary kinds of keys.[3]